Introduction
The Phantom 4 RTK from SZ DJI TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD is a professional-grade drone engineered for high-precision mapping, surveying, and aerial imaging. Built on DJI’s renowned Phantom platform, the Phantom 4 RTK integrates advanced real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning and a robust imaging system, making it a top choice for geospatial professionals and enterprise users who demand centimeter-level accuracy.
A critical milestone for any wireless device entering the U.S. market is FCC certification. The Phantom 4 RTK has achieved this with FCC ID SS3-WM334R1801, confirming its compliance with stringent radio frequency (RF) emission standards and legal eligibility for sale and operation in the United States. This certification assures users that the drone meets federal benchmarks for electromagnetic compatibility, reducing the risk of interference with other electronic devices.
In this article, we’ll break down the Phantom 4 RTK’s key features, technical specifications, wireless technologies, internal components, and regulatory insights. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, engineer, or enterprise buyer, this teardown and analysis will provide a comprehensive look at what sets the Phantom 4 RTK apart in the world of professional drones.
Key Features & Specifications
The Phantom 4 RTK stands out for its fusion of high-precision positioning, advanced imaging, and robust wireless communication. Let’s explore the standout features and core technical specifications that define this model.
Key Features
- Unprecedented Clarity & Image Quality:
Equipped with a 1-inch CMOS sensor camera, the Phantom 4 RTK delivers lower noise and exceptional image clarity, enabling precise data capture for mapping and surveying. - Return-to-Home Function:
Enhances operational safety by automatically returning the drone to its takeoff point in case of signal loss or low battery. - Remote Controller with Long-Range Transmission:
Offers a transmission range of up to 4.3 miles (7 km), providing flexibility for large-scale mapping missions. - Intelligent Flight Battery:
Smart battery management ensures reliable flight performance and efficient power usage. - Dual Frequency Support:
Supports dual-frequency operation for video downlink, boosting both the stability and quality of high-definition video feeds, even in challenging RF environments. - Replaceable Batteries and Antennas (Remote Controller):
Modular design allows for quick swaps, minimizing downtime in the field. - Stable Hover and Indoor Flight:
Advanced vision and infrared sensing systems enable precise hovering and safe operation indoors or in GPS-denied environments.
Technical Specifications
Vision & Sensing
– Obstacle Sensory Range: 2 – 98 ft (0.7 – 30 m)
– Infrared Sensing System Operating Environment:
Works on surfaces with diffuse reflection and reflectivity > 8%
Flight & Power
– Max Flight Time: Approx. 30 minutes
– Intelligent Flight Battery:
– Capacity: 5870 mAh
– Voltage: 15.2 V
– Type: LiPo 4S
– Energy: 89.2 Wh
– Net Weight: 468 g
– Remote Controller Intelligent Battery:
– Capacity: 4920 mAh
– Voltage: 7.6 V
– Energy: 37.39 Wh
– Charging Temperature: 5° to 40°C (41° to 104°F)
Camera
– Sensor: 1-inch CMOS, 20 megapixels effective
– Max Image Size: 16:9 Aspect Ratio: 5472 × 3078
– Lens: FOV 84°, 24 mm (35 mm equivalent), f/2.8–f/11, autofocus from 1 m to infinity
Wireless & Connectivity
– Bluetooth: Present (specific details not disclosed)
– Dual Frequency Video Downlink: Ensures robust HD video streaming and control at extended ranges
Practical Benefits
- Centimeter-Level Accuracy:
RTK positioning unlocks precise mapping and survey-grade results, minimizing ground control point (GCP) requirements. - Versatile Deployment:
The combination of long battery life, rugged sensor suite, and flexible wireless options supports a vast range of commercial and industrial applications. - User-Friendly Maintenance:
Modular batteries and antennas reduce servicing time and simplify logistics for large fleets.
Operating Frequencies
The Phantom 4 RTK (FCC ID SS3-WM334R1801) operates over several frequency bands, as detailed in its FCC filing. These frequencies are fundamental to its wireless communication, impacting range, reliability, and compliance with regulatory standards:
| Frequency Range (GHz) | Output Power (mW) | FCC Rule Part |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4775 | 619 | 15CCC2.25.7285 |
| 5.8465 | 164 | 15E38 |
| 12.4035–2.4775 | 505 | 15CCC2.12.4055 |
| 15.7305–5.8445 | 77 | 15E38 |
These allocations support the drone’s dual-frequency video downlink, command and control, and potentially Bluetooth and other telemetry functions. The output power levels are engineered for robust connectivity while staying within FCC limits to minimize interference.
Technology Deep Dive
The Phantom 4 RTK leverages a blend of advanced wireless technologies to provide seamless connectivity and precise navigation. Its primary wireless systems operate in the 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz bands—frequencies commonly used for Wi-Fi and proprietary RF links—ensuring both long-range control and stable high-definition video transmission. The presence of Bluetooth (as indicated in the specifications) likely supports quick device pairing or short-range configuration tasks.
The selected frequency bands and their respective power outputs directly influence the drone’s operational range, resistance to interference, and energy consumption. Higher output power at 2.4 GHz, for instance, enables more reliable connections in open environments, while dual-frequency support minimizes disruptions from crowded wireless spectra.
Test reports referenced in the FCC documentation confirm that the Phantom 4 RTK meets all relevant RF emission and immunity standards. The device’s careful frequency planning and shielding strategies ensure that mission-critical links—such as RTK corrections for centimeter-level positioning—are maintained even in electromagnetically noisy environments. Overall, the technology stack is optimized for professional-grade reliability, making the Phantom 4 RTK a standout in its class.
In-Depth Internal Component Analysis / Teardown
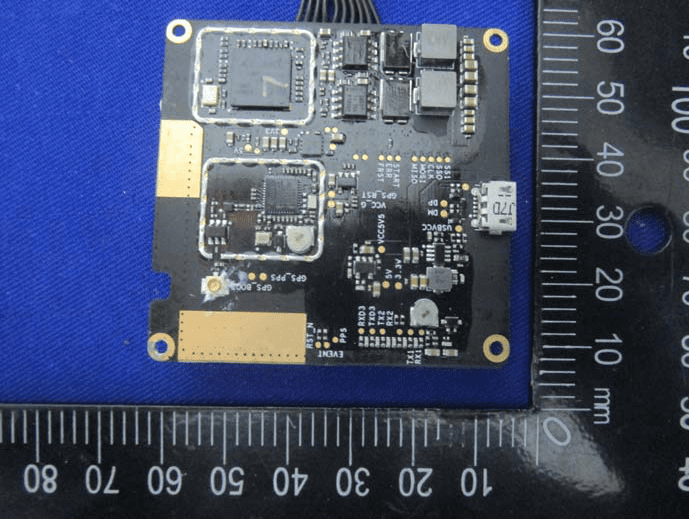
Main RTK/GNSS Module PCB
A close-up of the main internal PCB assembly reveals a meticulously engineered module at the heart of the Phantom 4 RTK’s positioning system. Two major ICs, each shielded under their own metal cans, dominate the board—likely a powerful SoC or GNSS receiver and a supporting RF front-end or microcontroller. This layout is essential for processing RTK corrections and maintaining signal integrity. The use of a black, high-grade FR4 PCB substrate, extensive via stitching, and controlled impedance traces underscores the board’s multi-layer, high-speed design. Gold-plated pads labeled for GPS antennas and a micro-USB port highlight the modularity and precision required for centimeter-level GNSS applications. Power delivery is robust, with multiple inductors and capacitors ensuring clean supply rails. The overall build quality, with its separation of analog and digital domains and heavy shielding, reflects DJI’s commitment to RF performance and reliability.
Sensor or IMU Interface Board
Examining a smaller, densely packed PCB module uncovers what is likely a sensor or IMU interface board. Its compact footprint and high component density suggest a critical role in the drone’s navigation suite. A prominent central IC, surrounded by precision passives and local power regulation, points to functions such as inertial measurement or sensor data aggregation. The gold-finished PCB and fine-pitch connectors indicate a high-speed data path, essential for real-time flight control and stabilization. Differential pairs and robust ground planes ensure signal integrity, while the absence of RF components confirms its focus on sensor interfacing rather than communication. The craftsmanship, including tight soldering and modular connectors, supports DJI’s philosophy of reliability and maintainability.

Auxiliary Control or Sensor Module
A further detailed look at another compact PCB reveals a board populated with several ICs, including a medium-sized QFP or QFN package likely serving as a microcontroller or sensor interface. The arrangement of passive components, local power regulation, and a precision crystal oscillator suggest functions related to timing, data acquisition, or auxiliary control. The high density of vias and multi-layer construction support both analog and digital operations, with careful routing to minimize noise. A fine-pitch connector and multiple test points highlight the board’s integration into the larger system, facilitating diagnostics and updates. This module exemplifies the modular, high-performance approach DJI employs across the Phantom 4 RTK’s subsystems.

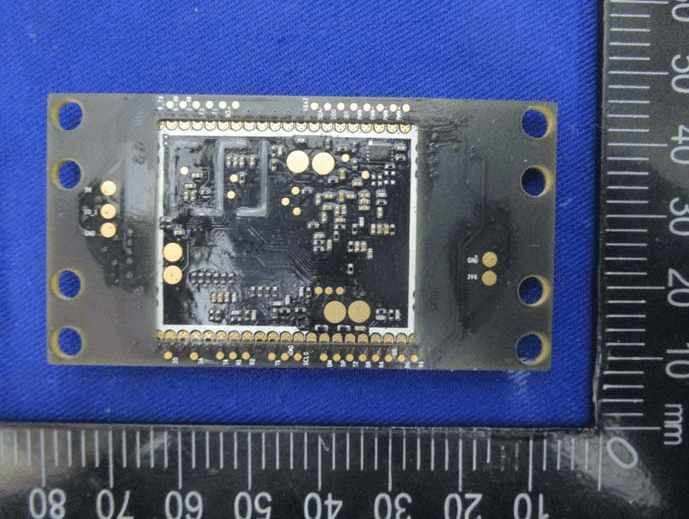
High-Density Internal Module
The underside of another internal module showcases a dense array of passive components and solder pads, likely for a BGA or LGA IC on the opposite side. The layout, with extensive via stitching and large mounting holes, suggests this is a core processing or RF board. The multi-layer design supports high-speed or sensitive signal transmission, while robust grounding and mechanical stability are prioritized. The lack of visible antennas or major power components on this face indicates this board is a subassembly, interfacing with other modules for critical functions such as GNSS processing or communications. The overall design reflects DJI’s focus on signal integrity and reliability for mission-critical drone operations.
Regulatory Insights & FCC Filing
The FCC ID SS3-WM334R1801 assigned to the Phantom 4 RTK is a testament to its adherence to U.S. regulations on electromagnetic compatibility and RF emissions. This certification, registered through FCC.gov, is a legal prerequisite for sale and operation in the U.S. and ensures the drone will not cause harmful interference with other electronic devices or communication systems.
FCC filings for the Phantom 4 RTK provide a wealth of technical information, including comprehensive test reports for RF exposure and electromagnetic compatibility, internal and external photographs, user manuals, schematics, and block diagrams. These documents reveal the rigorous testing and engineering that underpin the device’s compliance.
According to the user manual and internal documentation, the Phantom 4 RTK is purpose-built for high-precision mapping, equipped with advanced obstacle avoidance, centimeter-level RTK positioning, and a professional-grade camera. The FCC test reports confirm the drone’s ability to operate within allocated frequency bands and output power limits, reinforcing its suitability for demanding enterprise applications. This regulatory transparency not only assures end-users of legal compliance but also demonstrates DJI’s commitment to quality and safety.
Potential Use Cases & Target Audience
The Phantom 4 RTK’s unique combination of precision, imaging, and robust wireless capabilities opens the door to a range of professional applications:
- Aerial Mapping and Surveying:
Geospatial professionals can leverage the drone’s RTK accuracy and high-resolution camera to produce detailed maps and 3D models for construction, mining, or land management. The reduced need for ground control points streamlines workflows and increases efficiency. - Precision Agriculture:
The Phantom 4 RTK enables the creation of orthomosaic maps for crop analysis, field planning, and integration with agricultural drones like the Agras MG-1S Advanced or MG-1P series. Accurate maps support precision spraying, yield estimation, and informed decision-making. - Infrastructure Inspection:
Utility companies, engineers, and surveyors benefit from the drone’s stable hover, advanced obstacle avoidance, and long-range video downlink to inspect bridges, power lines, and buildings safely and efficiently, even in GPS-denied or indoor environments.
These use cases highlight the Phantom 4 RTK’s value for professionals who demand accuracy, reliability, and efficiency in aerial data acquisition.
Conclusion
The Phantom 4 RTK by SZ DJI TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD (Model: Phantom 4 RTK, FCC ID SS3-WM334R1801) stands as a benchmark in precision drone technology. Its fusion of advanced RTK positioning, high-quality imaging, robust wireless performance, and thoughtful modular design sets it apart in the enterprise drone market. With proven regulatory compliance, as evidenced by its FCC certification, the Phantom 4 RTK is not only legal for use in the U.S. but also exemplifies engineering excellence for demanding professional applications. For those seeking reliable, centimeter-level mapping and data capture, the Phantom 4 RTK is a clear leader in its class.