Introduction
The DJI WIND-4 is a professional-grade, customizable unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) platform engineered for demanding industrial and commercial applications. Developed by DJI—an industry leader in aerial robotics—the WIND-4 offers robust flight performance, modular accessory compatibility, and advanced operational safety features. Its primary function is to serve as a flexible aerial platform, adaptable for tasks ranging from industrial inspection and mapping to payload delivery and public safety operations.
Crucially, the WIND-4 (Model: WIND-4) has achieved FCC certification under the ID SS3-WIN81803. This certification is more than a regulatory formality: it confirms the device’s compliance with stringent U.S. RF emission standards, making it legal to sell and operate within the United States. FCC approval ensures that the WIND-4 does not cause harmful interference and meets safety guidelines for electromagnetic emissions.
This article delivers a comprehensive, expert-level analysis of the DJI WIND-4, focusing on its key features, technical specifications, wireless technology, internal components, and regulatory compliance. Whether you’re an engineer, UAV developer, or an advanced user, read on for a deep dive into what sets the WIND-4 apart in the professional drone market.
Key Features & Specifications
The WIND-4 by DJI is engineered for versatility, safety, and high performance in professional UAV operations. Its design emphasizes reliability, expandability, and advanced power management—attributes critical for demanding use cases.
Key Features
- Accessory Compatibility
- Fully compatible with supply boxes, megaphones, and a range of developer accessories, enabling mission-specific customization.
- Over Current Protection
- Safeguards electronics and batteries from damage due to excessive current draw.
- Short Circuit Protection
- Enhances operational safety by preventing system-wide failures during electrical faults.
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button and LED
- Provides an immediate failsafe for autonomous return, improving safety in mission-critical scenarios.
- Battery Cell Damage Protection
- Monitors and protects battery health, maximizing lifespan and minimizing risk.
- Auto Start Function
- Streamlines pre-flight checks and launches, reducing operator workload and error.
- Camera Settings Dial
- Allows in-flight camera adjustments, crucial for aerial imaging and inspection tasks.
- Remote Controller GPS Module
- Integrates precise location tracking for improved navigation and control reliability.
Technical Specifications
- Battery & Power
- Charging temperature: 0°C to +40°C (32°F to 104°F)
- Battery over discharge protection voltage: 38.4 V
- Battery charging current: Recommended 1C (12 A), Maximum 2C
- Battery sleep mode: Activates after 20 minutes of not being connected to the aircraft
- Battery auto-discharge: Reduces charge to below 65% after 10 days idle (process takes ~2 days)
- Remote controller battery: 2S rechargeable, 6000 mAh capacity
-
Main battery: 44.4 V, 12000 mAh
-
Environmental & Flight
- Operating temperature range: -10°C to +40°C (14°F to 104°F)
-
Maximum operating altitude: 9,843 feet (3,000 meters) above sea level
-
Wireless & Control
- Remote controller maximum signal transmission range: 3 km
- Bluetooth: Present (details N/A)
Practical Implications
These specifications underscore the WIND-4’s suitability for professional missions in challenging environments. Over-current and short-circuit protection, along with advanced battery management, ensure operational safety and longevity. The modular accessory interface enables rapid deployment for a wide range of tasks, while the robust wireless link (up to 3 km) ensures reliable control in the field.
Operating Frequencies
The DJI WIND-4 (FCC ID SS3-WIN81803) operates on the following frequencies, as detailed in its FCC filing:
| Frequency Range (GHz) | Output Power (mW) | FCC Rule Part |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4065–2.4765 | 341 | 15CMO1 |
These frequencies fall within the globally recognized 2.4 GHz ISM band, commonly used for drone communications, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. The output power of 341 mW supports robust, interference-resistant links suitable for professional UAV operations.
Technology Deep Dive
The WIND-4 leverages advanced wireless technologies within the 2.4 GHz ISM band, aligning with industry standards for UAV control and telemetry. While the primary equipment class does not specify cellular capability, the device’s frequency allocation and output power are consistent with high-performance proprietary RF links, such as DJI’s Lightbridge 2 system, as well as Bluetooth for close-range configuration and diagnostics.
Operating in the 2.4 GHz band allows the WIND-4 to balance range, data throughput, and interference resilience. The specified output power (341 mW) is well above that of consumer Wi-Fi or Bluetooth devices, supporting a strong and reliable connection over distances up to 3 km—critical for industrial and enterprise missions. The use of spread-spectrum or frequency-hopping techniques (implied by the rule part and typical DJI implementations) further enhances resistance to interference from crowded ISM spectrum environments.
Test reports referenced in the FCC filing confirm compliance with regulatory emission limits, ensuring that the WIND-4 can operate safely alongside other wireless devices. The integration of Bluetooth, although not detailed, likely supports device setup, maintenance, or accessory communication without impacting mission-critical flight control channels.
In-Depth Internal Component Analysis / Teardown
Power Management & Distribution Board
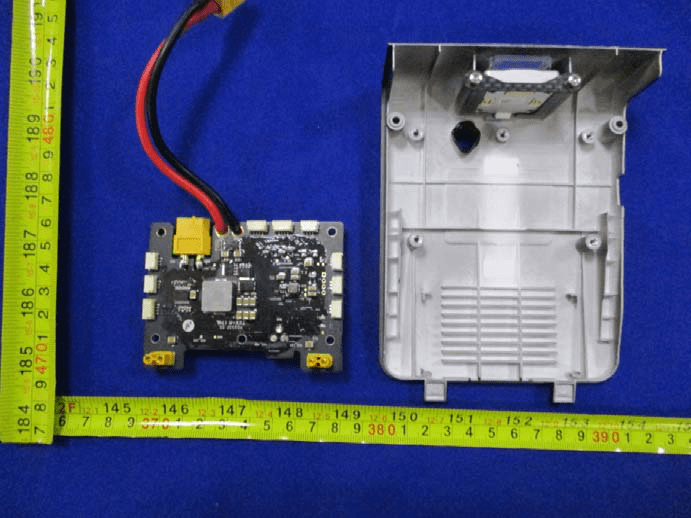
A detailed inspection of the WIND-4’s internal power management module reveals a densely populated black PCB, indicative of high-quality FR4 material and robust engineering. Central to the board is a large QFP/QFN integrated circuit, almost certainly responsible for power management or as the primary system controller. Surrounding this are several smaller ICs—likely MOSFETs or power drivers—positioned near the board’s edges to manage high-current switching or sensing. The thick red and black wires, along with an XT60 connector, signal the board’s role in main battery interfacing and power distribution. Multiple white edge connectors facilitate modular connections to motors, sensors, or ESC subsystems. The absence of RF components and the presence of substantial capacitors and inductors underscore its focus on power handling rather than communications. Overall, the PCB’s compact layout, robust ground planes, and careful via placement reflect a design optimized for reliability, EMI control, and easy field servicing—hallmarks of a high-end drone power subsystem.
Multi-Phase Motor Control (ESC) Board
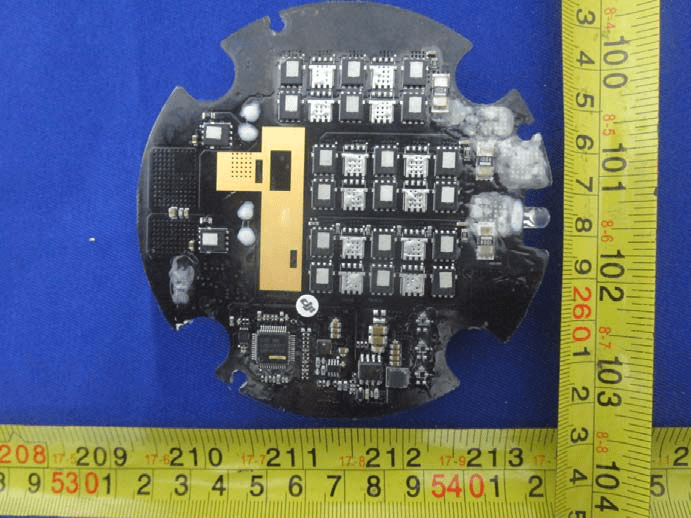
The circular PCB examined here is a striking example of sophisticated electronic speed controller (ESC) design, tailored for UAV propulsion. Featuring a grid of identical ICs—almost certainly power MOSFETs or motor drivers—this board is purpose-built for multi-phase motor control, a necessity for precise and efficient drone flight. The lower segment contains a larger QFP/QFN package, likely a microcontroller or specialized gate driver, orchestrating the rapid switching required for brushless motor operation. The use of a black ENIG-finished PCB, multiple vias, and wide copper pours signals a high-reliability, multi-layer design. Heavy-gauge solder pads and connectors accommodate the substantial currents needed for flight, while the presence of conformal coating suggests environmental protection. The absence of RF components reinforces its role as a high-performance ESC rather than a communications module. This level of integration and attention to power integrity is essential for the demanding operational envelope of the WIND-4.
Precision Sensor/Interface Module
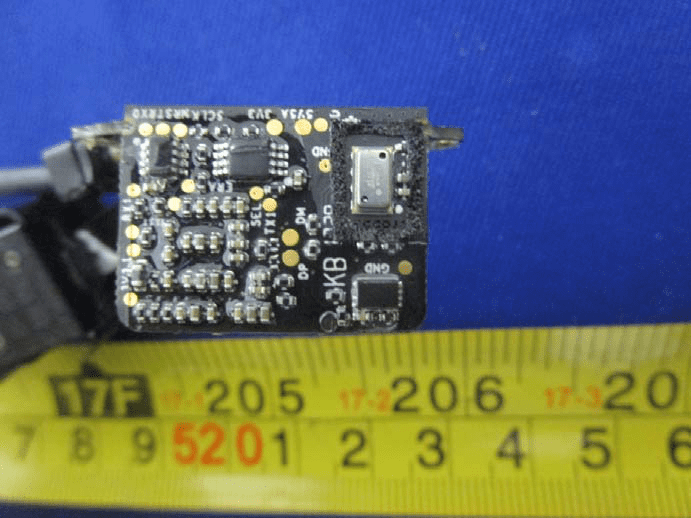
This compact PCB is engineered for sensing and interfacing within the WIND-4’s modular avionics suite. The board hosts several small-outline ICs, likely including a microcontroller or analog front-end for sensor data acquisition, with silkscreened labels such as SCL/SDA hinting at I2C or SPI digital communication. The presence of a metal-can MEMS sensor—potentially an accelerometer, gyroscope, or barometer—underscores its role in flight stabilization or environmental monitoring. Dense SMD component placement, robust ground connections, and multiple labeled test points reflect a meticulous design for low-noise signal processing and ease of debugging. The multi-wire cable interface suggests integration with the main flight controller, providing vital real-time data for navigation or payload management. This module exemplifies best practices in UAV sensor electronics, combining reliability, precision, and compactness for mission-critical applications.
Regulatory Insights & FCC Filing
The FCC ID SS3-WIN81803 is a testament to the WIND-4’s adherence to rigorous U.S. regulatory standards for wireless devices. Registered with the FCC, this certification affirms the device’s compliance with electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radiofrequency (RF) emission limits, making it lawful to market and operate the WIND-4 in the United States.
FCC filings for the WIND-4 typically encompass comprehensive test reports (RF exposure, EMC), internal and external photographs, user manuals, block diagrams, and schematics. These documents collectively verify that the UAV’s wireless subsystems and power electronics do not cause harmful interference and are safe for both operators and bystanders.
Key insights from the user manual and internal documentation reveal that the WIND-4 is a professional, modular UAV platform featuring advanced flight control, propulsion, and transmission systems. The documentation highlights its compatibility with a variety of developer accessories and emphasizes operational safety through features like over-current, short-circuit, and battery cell damage protection. The FCC test reports confirm that the device meets all relevant emission standards, supporting its use in critical, interference-sensitive environments.
Potential Use Cases & Target Audience
The DJI WIND-4 is purpose-built for professional users who demand reliability, flexibility, and advanced safety in aerial operations. Its robust platform, modular accessory compatibility, and industry-leading technology make it ideal for a variety of high-value applications:
-
Industrial Inspection & Surveying
Companies in energy, infrastructure, and construction can deploy the WIND-4 for aerial inspection, mapping, and surveying. The ability to integrate specialized payloads—such as supply boxes, sensors, or cameras—maximizes mission versatility. -
Public Safety & Emergency Response
Equipped with megaphones, supply delivery modules, or thermal imaging payloads, the WIND-4 serves as a force multiplier for search and rescue, disaster assessment, and law enforcement. -
Developer & Research Applications
For R&D teams and solution developers, the WIND-4 offers a customizable flight platform with open interfaces for accessory integration, making it an excellent testbed for new UAV technologies and mission-specific solutions.
With a clear focus on professional markets, the WIND-4 is not intended for consumer or recreational use, nor is it suitable for operators under 18 years of age.
Conclusion
The DJI WIND-4 (Model: WIND-4, FCC ID SS3-WIN81803) stands out as a professional, adaptable UAV platform engineered for demanding applications. Its FCC certification under SS3-WIN81803 underscores strict compliance with U.S. RF emission and safety standards, ensuring legality and reliability. With advanced power management, modular design, and robust wireless capabilities, the WIND-4 is well-positioned to meet the needs of industrial, public safety, and research users seeking a high-performance aerial solution. As UAV technology continues to evolve, the WIND-4 exemplifies the integration of regulatory compliance, engineering excellence, and functional versatility.