Remote Control by SZ DJI TECHNOLOGY: A Comprehensive Analysis of FCC ID SS3-WM300U24G
Introduction
SZ DJI TECHNOLOGY, a leader in drone and remote control technology, has introduced a new Remote Control model, the WM300U24G. This device, bearing the FCC ID SS3-WM300U24G, is designed to meet high standards of performance and regulatory compliance. While the FCC grant date is not specified, the certification signifies that the device complies with RF emission standards, making it legal for sale and use in the United States. In this blog post, we will explore the key features, technical specifications, and internal components of this remote control. Additionally, we’ll delve into the operating frequencies and regulatory insights that underscore its market readiness.
Key Features & Specifications
The Remote Control by SZ DJI TECHNOLOGY is engineered for precision and reliability. While official detailed specifications are sparse, typical expectations for such a device include:
- High-Frequency Communication: Operates in the 2.4GHz band, which is standard for remote controls, ensuring robust and interference-free communication.
- Compact and Ergonomic Design: Designed for ease of use, with intuitive button layout and control sticks for seamless user interaction.
- Battery-Powered: Utilizes a lithium polymer battery, delivering long-lasting power for extended operation.
- RF Shielding: Features metal shields to protect sensitive components from electromagnetic interference, enhancing performance stability.
- External Antenna: Equipped with a white external antenna for improved signal transmission and reception.
These features collectively make the remote control a reliable tool for controlling drones or other devices requiring precise input and communication.
Operating Frequencies
The Remote Control operates on specific frequencies as detailed in its FCC filing:
| Frequency Range (GHz) | Output Power (mW) | FCC Rule Part |
|---|---|---|
| 2.405375-2.477055 | 66.4 | 15C1 |
These frequencies ensure the device adheres to regulatory standards, providing reliable wireless capabilities essential for remote operation.
Technology Deep Dive
The Remote Control leverages wireless technologies typically found in consumer electronics, such as Wi-Fi or proprietary RF protocols. The operating frequencies allow for a balance between range and power consumption, with sufficient bandwidth for control signals. The device’s design prioritizes performance, with considerations for minimizing interference and optimizing power efficiency. Such capabilities are crucial for maintaining stable connections in various environments, from urban settings to open fields.
In-Depth Internal Component Analysis / Teardown
The internal architecture of the Remote Control is a testament to its sophisticated engineering. Below are detailed analyses of its internal components based on provided images:
-
The PCB in the first image showcases several ICs, including a prominently shielded one, likely an RF transceiver or SoC critical for communication. The multi-layer board suggests high integration, with a focus on compactness. The external antenna and robust shielding highlight the emphasis on reliable RF performance.
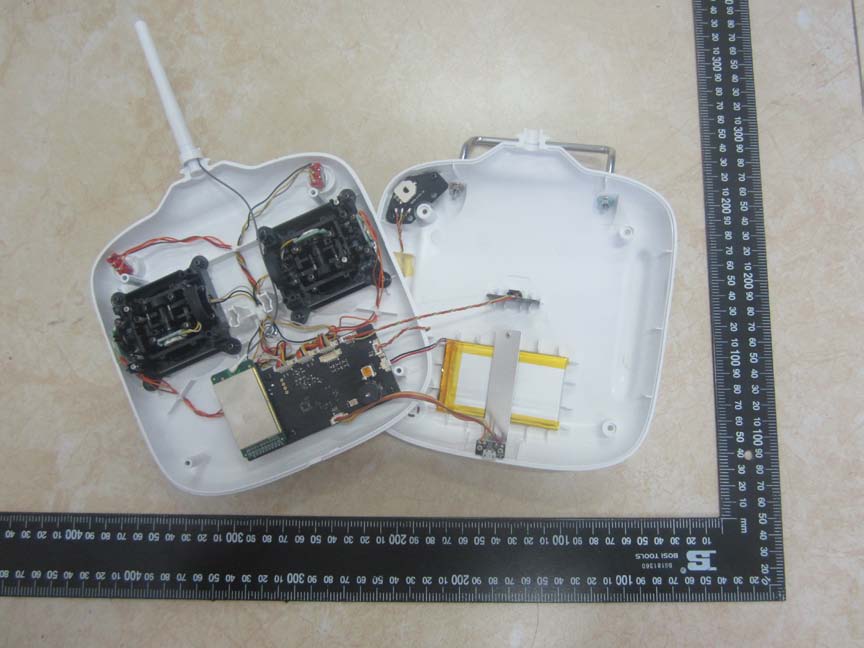

Main PCB with RF shielding and external antenna. -
Another image reveals a PCB with several ICs, possibly including an MCU or SoC for processing. The layout is compact, with an external antenna for 2.4GHz communication, emphasizing signal integrity and space efficiency.
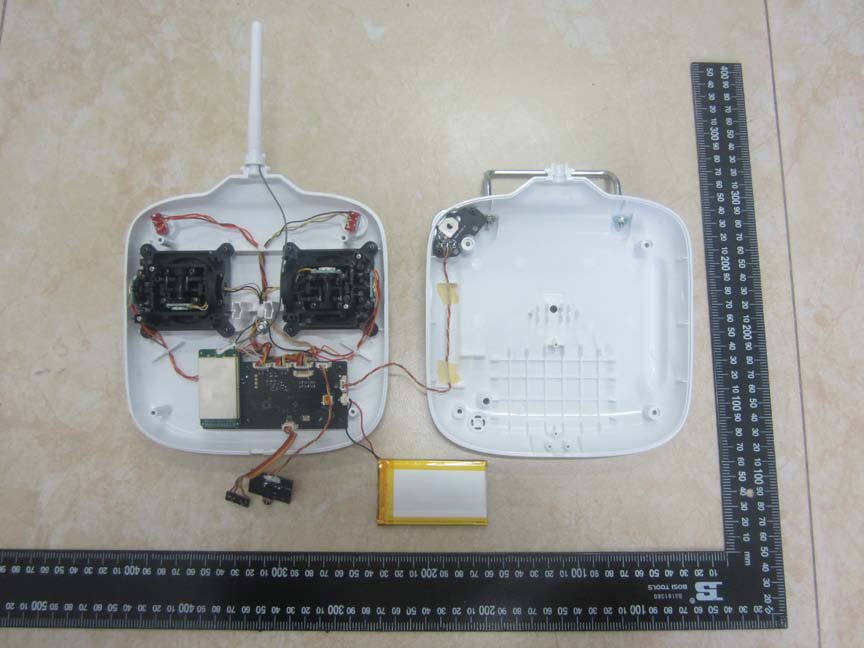

PCB with MCU/SoC and external antenna connection. -
A multi-layer PCB in the next image features a shielded section likely housing RF components. Multiple connectors suggest modularity, with power management indicated by visible capacitors and inductors.
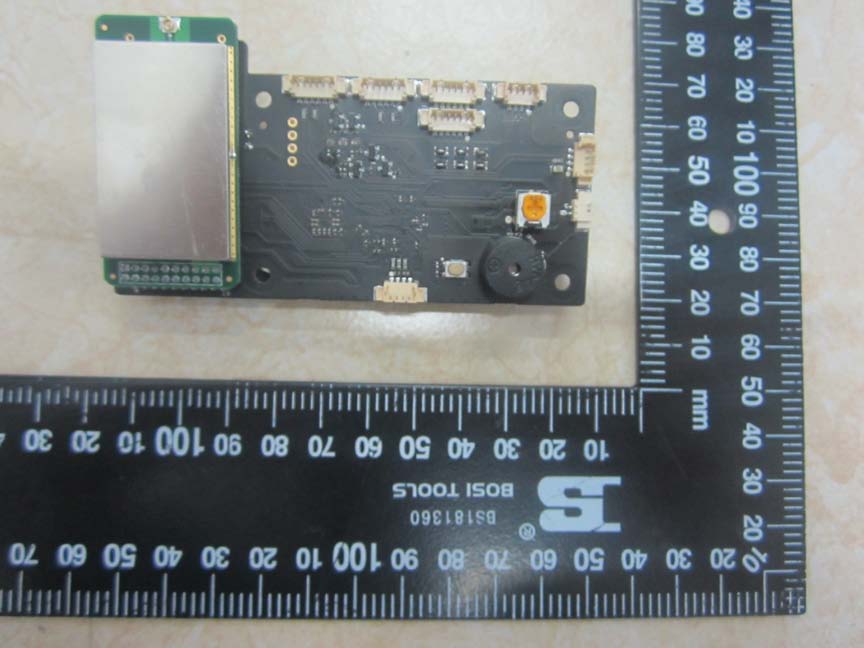

Multi-layer PCB with RF shielding and modular connectors. -
The subsequent image shows a single-sided board with connectors and passive components, indicating a focus on interfacing and control. The presence of a small speaker suggests audio feedback capability.

Single-sided PCB with connectors and speaker for feedback. -
Another board features several ICs, likely including a central microcontroller for signal processing. The compact layout and connectors suggest this board interfaces with other system modules.
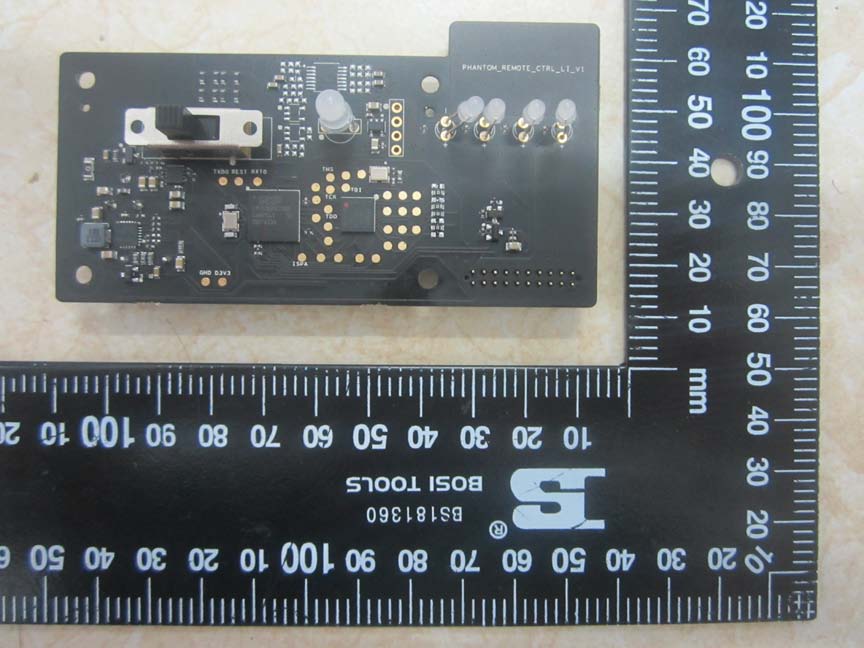
Compact PCB with microcontroller and system interface connectors. -
The final image highlights a PCB with a prominent IC, possibly an RF transceiver. The U.FL connector indicates an external antenna connection, enhancing modularity and performance flexibility.

RF module PCB with U.FL connector for external antenna.
Regulatory Insights & FCC Filing
The FCC ID SS3-WM300U24G signifies compliance with US electromagnetic interference standards, allowing for its legal sale and use. The FCC filing typically includes test reports for RF exposure, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), internal photos, user manuals, schematics, and block diagrams. These documents ensure that the device meets safety and performance standards, providing consumers with assurance of quality and reliability.
Potential Use Cases & Target Audience
The Remote Control’s robust features and compliance make it ideal for various applications:
- Drone Enthusiasts: Perfect for hobbyists and professionals seeking precise control over their aerial devices.
- Industrial Operators: Suitable for controlling machinery or equipment in industrial settings, where reliable communication is critical.
- Tech-Savvy Consumers: Appeals to users interested in cutting-edge remote control technology for home automation or custom projects.
Conclusion
The Remote Control by SZ DJI TECHNOLOGY, with its FCC ID SS3-WM300U24G, represents a blend of sophisticated technology and regulatory compliance. Its design emphasizes reliability, performance, and user interaction, making it a valuable tool in its market segment. As the landscape of remote control technology evolves, this device stands out for its robust engineering and compliance with industry standards.