Unveiling the Ronin by DJI: An In-Depth Analysis of FCC ID SS3-HG9001407
Introduction
The Ronin by DJI is an advanced camera stabilization system designed to elevate the art of cinematography. Known for its precision and versatility, the Ronin provides filmmakers with unparalleled control and stability, essential for capturing smooth and dynamic footage. Bearing the FCC ID SS3-HG9001407, this device meets stringent standards for radio frequency emissions, ensuring it is both safe and legal for use in the United States. In this article, we’ll delve into the key specifications, internal components, and regulatory aspects of the Ronin, providing a comprehensive overview of its capabilities and technological innovations.
Key Features & Specifications
The Ronin’s standout feature is its brushless gimbal stabilization system, which ensures smooth and stable footage even in challenging conditions. Here are some of the key features and specifications that make the Ronin a must-have for professional cinematographers:
Key Features:
– Brushless Gimbal Stabilization System: Provides seamless stabilization for a wide range of camera sizes and weights.
– Three Operation Modes: Includes underslung, upright, and briefcase modes for versatile shooting angles.
– Position Feedback and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Ensures precise control and stability.
– Custom 32-bit Processor: Delivers high-speed performance and accurate movement translation.
Technical Specifications:
– Maximum Run Time: 4 hours
– Battery Capacity: 3400mAh
– Voltage: 14.8V
– Bluetooth: Present (Details N/A)
These features and specifications highlight the Ronin’s commitment to delivering world-class stabilization technology, making it an essential tool for filmmakers seeking precision and reliability.
Operating Frequencies
The Ronin operates on the following frequencies as detailed in its FCC filing:
| Frequency Range (GHz) | Output Power (mW) | FCC Rule Part |
|---|---|---|
| 12.402-2.48 | 2.3 | 15C2.1 |
Understanding these operating frequencies is crucial for assessing the Ronin’s wireless capabilities, including its range and adherence to regulatory standards for RF communications.
Technology Deep Dive
The Ronin employs advanced wireless technologies to facilitate seamless connectivity and control. The presence of Bluetooth, as indicated in its specifications, suggests integration for remote control and configuration tasks. The specified operating frequencies ensure that the Ronin can operate efficiently within regulatory limits, minimizing interference and optimizing power consumption. These technologies enable the Ronin to deliver precise control and stability, essential for professional-grade cinematography.
In-Depth Internal Component Analysis / Teardown
The internal components of the Ronin by DJI reveal a sophisticated design optimized for performance and reliability. Below is an expert analysis of the device’s internal hardware based on detailed component photographs.
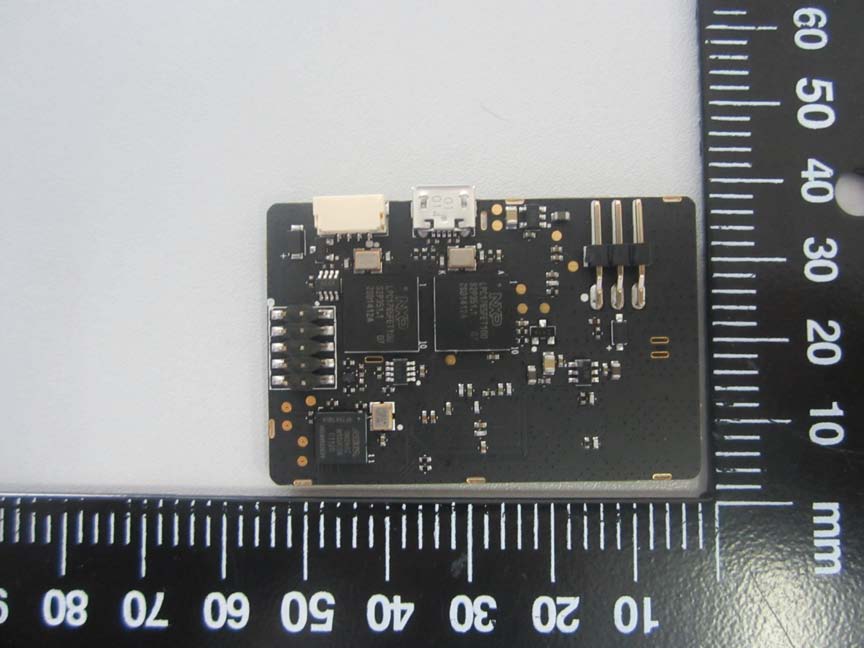
The image reveals a densely populated PCB featuring multiple integrated circuits (ICs) responsible for various functions such as motor control, power management, and communication. The board’s multi-layer design, likely consisting of 4-6 layers, suggests a complex setup with differential pairs and impedance-controlled traces for high-speed data or RF signal routing. The presence of a PCB trace antenna indicates RF communication capabilities, possibly for Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Visible connectors facilitate connections to other modules, while power regulation components ensure stable power delivery. Overall, the design reflects a focus on efficient power management and reliable communication, critical for a gimbal system like the Ronin.

The compact PCB shown in this image hosts several ICs, likely including a microcontroller or SoC for processing and motor drivers given the device’s function. The absence of antennas suggests that wireless communication might be handled elsewhere. The board’s multi-layer design and dense routing indicate a sophisticated setup, with connectors for interfacing with sensors or control boards. The lack of visible shielding suggests reliance on the enclosure for EMI/RFI protection. Overall, the design is optimized for motor control and stabilization, consistent with the Ronin’s role as a gimbal system.

This PCB features a microcontroller or specialized IC, likely for motor control or communication. Its simple layout and lack of complex via structures suggest a single or double-layer design. Connectors indicate integration into a larger system, while power connections are evidenced by red and black wires. The straightforward layout suggests a focus on reliability and ease of assembly, essential for a gimbal system requiring precise control and stability.
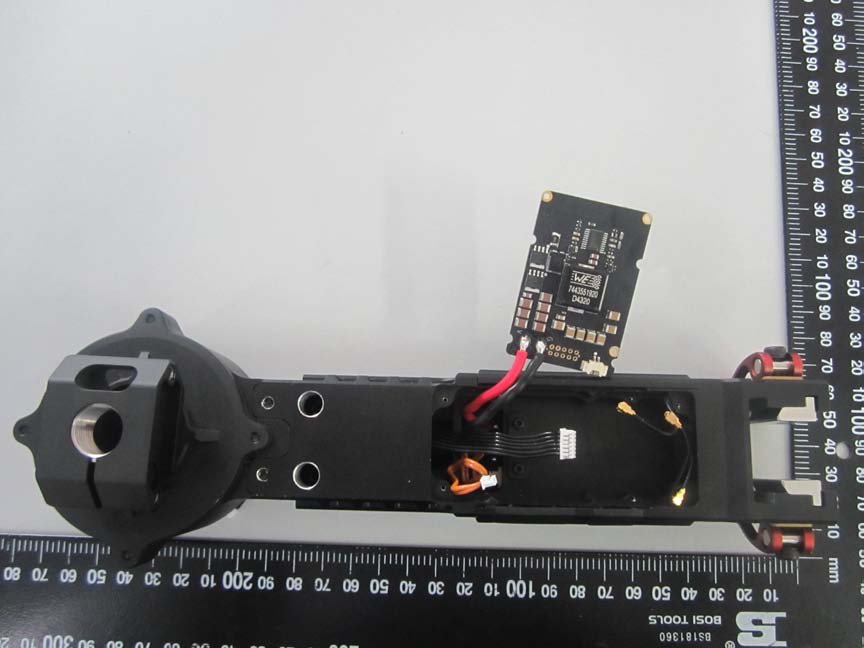

The board displays a high level of integration with several ICs, including a microcontroller or SoC for control tasks. The multi-layer design and differential pair routing suggest a focus on high-speed data handling. Connectors for external antennas and a USB interface highlight the device’s modularity and connectivity. This design supports functions related to control and communication, aligning with the Ronin’s purpose as a stabilization system.

This multi-layer PCB houses several ICs, including potential microcontrollers or processors from vendors like ARM. The layout incorporates both digital and analog components, with connectors for data transfer or charging. The absence of visible antennas suggests they are located elsewhere. The design emphasizes modularity and integration, crucial for the Ronin’s role in providing precise control and communication.
Regulatory Insights & FCC Filing
The FCC ID SS3-HG9001407 signifies the Ronin’s compliance with US electromagnetic interference standards, allowing it to be legally sold and used. Although the grant date is not specified, the device’s registration with the FCC ensures it meets safety and performance requirements. FCC filings typically include test reports for RF exposure and electromagnetic compatibility, as well as photos, manuals, schematics, and block diagrams, providing comprehensive documentation of the device’s compliance and capabilities.
Potential Use Cases & Target Audience
The Ronin’s advanced stabilization technology and versatility make it ideal for professional cinematographers seeking world-class movement translation and stability. With control and stability accuracy down to 0.02 degrees of translated movement, the Ronin caters to filmmakers who require precise camera control for dynamic shots. Its ability to accommodate a broad spectrum of cameras varying in size and weight makes it suitable for diverse filming scenarios, from indie films to major productions.
Conclusion
The Ronin by DJI, with its FCC certification (ID: SS3-HG9001407), represents a pinnacle of camera stabilization technology. Its sophisticated design and robust feature set make it an invaluable tool for filmmakers seeking precision and reliability. As a testament to DJI’s engineering prowess, the Ronin stands out in the market as a leading solution for professional cinematography, ensuring that every shot is captured with unparalleled stability and control.